Wednesday, 29 November and Thursday, 30 November, 2006





Using information from the videos from activities and laboratory activities
Students should be able to:
-demonstrate how speed is affected by contact forces.
-hypothesize, test, and draw conclusions from an experiment.
Our do now was a quick write: Why do some shoes have textured soles?
After reviewing past home learnings, we completed lab 10 on friction and speed, to access how friction affects the acceleration of an object. Students concluded that friction causes objects to move slower and to stop. As an alternataive to this lab, students should first print out the individual investigations sheets from the geocities site, and then visit the following site:
http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/E24/E24.html
Be sure to answer all the journal questions and to complete the table.
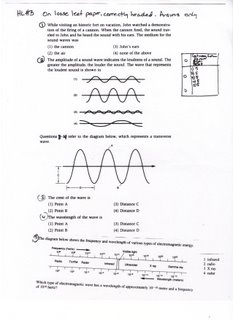
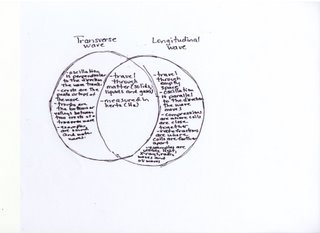
Home learning can be found at the top of this blog. HL 8 and HL 9 should be done on separate sheets of loose leaf paper. Be sure to label each section and place only answers on your sheets. You should have two separate sheets to turn in!